
Ransomware is an aggressive form of computer virus that targets your server, encrypts files and then demands a ransom for their release.
The technology driving ransomware - such as the CryptoLocker - is increasingly advanced and difficult to detect. It often targets the human element, relying on tricking a user into interacting with an innocuous looking file or link. Even with regular training, it only takes a single momentary lapse in judgement from a user to result in an infection. Given the volume of sensitive data that schools hold relating to children and their very strong reliance on data, this represents a significant threat to safeguarding. Following on from our Top 10 tips to protect your school from computer viruses, below is further advice on safeguarding your school data.How can ransomware infections occur?
There are four main ways to be aware of:
- Spam and unsolicited email: An easy and popular way for ransomware to spread is via emails and unsolicited email attachments. The emails trick the user into opening it, or opening the attachments (usually by making the content appear enticing for the user).
- Infected removable drives: Malware can spread through removable drives (USB flash drives and external hard drives). It is usually created to automatically install on any machine that it is connected to. If a computer or any other type of device is connected to a network, the malware can spread through the network to other machines.
- Bundled with other software: Ransomware can be bundled together with other software applications that are downloaded and installed. The victim may think they are only downloading a certain legitimate application, not knowing that it is a Trojan horse designed to trick them into activating the malware on their device.
- Compromised webpages: Ransomware can take advantage of software vulnerabilities in order to infect a computer. When the victim visits a compromised or hacked website, the ransomware can utilise pop-ups or other malicious tactics that mimic online advertisements in order to engage with the victim. Sometimes not even a click is needed for the ransomware to covertly seize control of the computer.
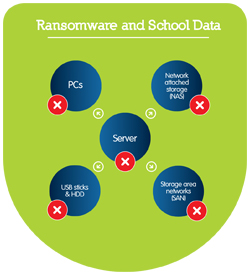
Once it has targeted your server, the ransomware will seek and infect all onsite data storage, as depicted above.
How can SBS help?
Service Desk support
If you are concerned that you have been targeted by ransomware or any type of virus, please call us on 0345 222 1551 • Option 1 (existing ICT customers) or 0345 222 1551 • Option 5 (non-ICT customers).Disaster Recovery Solution - Be proactive and backup your data offsite
The safeguarding of critical data is our primary concern and we don't want schools to pay to get their files back. With this in mind we have developed a Disaster Recovery Solution to backup, secure and restore data in the event of an attack from ransomware. For more information, call 0345 222 1551 • Option 5 or email us, and we can recommend the amount of storage you need to backup your files offsite and out of reach of virtual threats.Further reference - Ransomware and UK institutions
Almost 60% of higher education institutions have suffered an attack in the past year, while a high-profile case involving Lincolnshire County Council resulted in having to shut down their systems for several days and being hit with a £1 million ransom demand. Given the volume of sensitive data that schools hold relating to children and their very strong reliance on data to function, this represents a significant threat to safeguarding. There are steps that you can take to minimise the risks of ransomware to your establishment and to make sure your school’s data is protected. Additionally, Bournemouth University has been hit 21 times in one year by ransomware.Get sector Insights delivered straight to your inbox.
Subscribe to to the SBS Blog and never miss an update.

